NTC Thermistor Automotive: Choosing Between NTC and PTC for Vehicles
Sep 24, 2025Modern vehicles use dozens of temperature sensors. Battery packs, power electronics, motors, coolant and cabin systems all rely on accurate sensing. Choosing the right component reduces warranty risk, improves safety, and lowers system cost. The two most common thermistor families are NTC thermistors and PTC thermistors. Each serves distinct roles: NTC devices for precise measurement, PTC devices for protection and self-regulation.
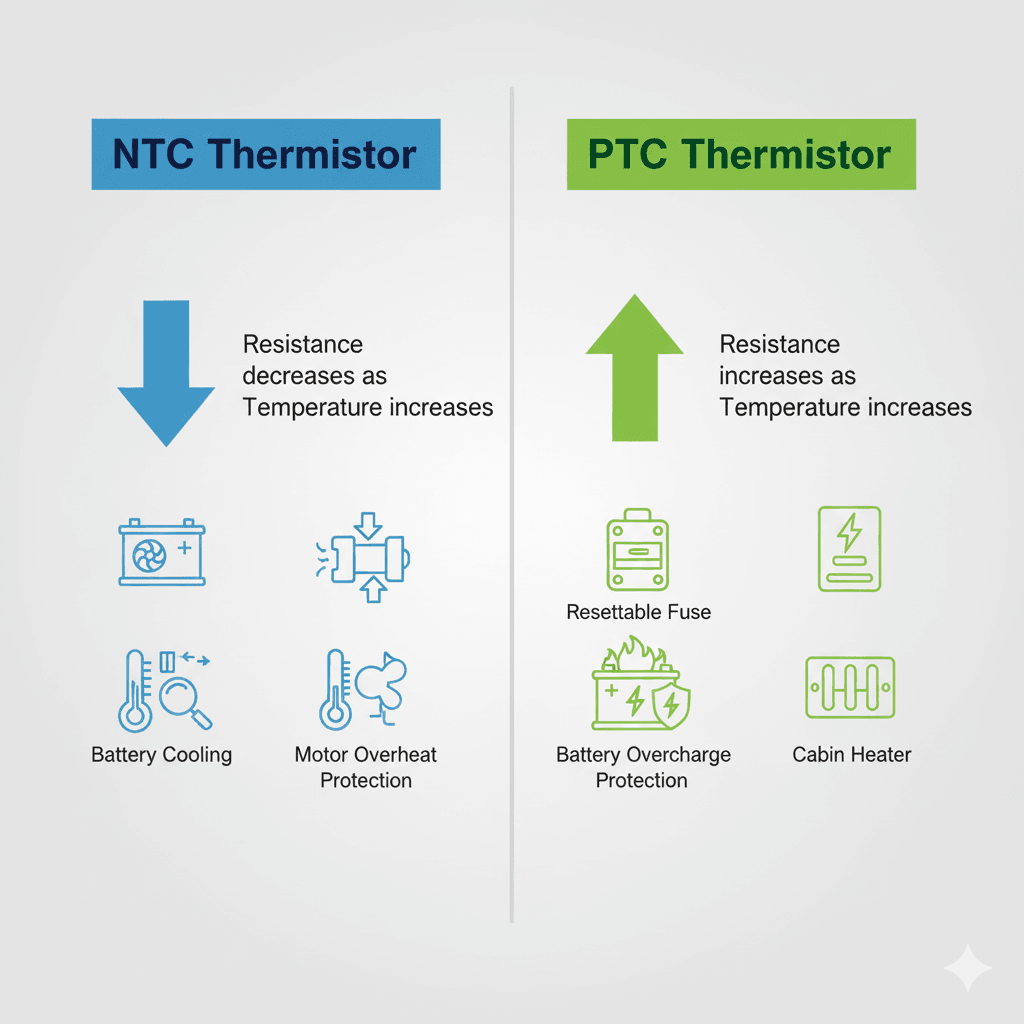
An NTC thermistor automotive device has a resistance that decreases as temperature rises. NTC materials are typically metal-oxide ceramics. They are highly sensitive at specific ranges and offer fine resolution for control systems. Typical uses include cell-level temperature monitoring in EV batteries, coolant sensing, and air temperature feedback for HVAC systems.
PTC thermistor devices increase resistance when temperature rises. Many PTC parts are designed to “switch” around a threshold, which makes them useful as resettable fuses, inrush current limiters, or self-regulating heating elements. In automotive systems, PTC thermistors are commonly found in motor protection circuits, cabin heaters, and pre-charge applications.
When sourcing sensors, buyers must compare parameters rather than brand claims. Below are the technical factors that matter most.
NTC thermistors usually operate accurately between −55°C and +150°C, with some specialized types rated to wider extremes. PTC parts used for protection can tolerate higher surface temperatures but are specified by switching thresholds rather than linear accuracy.
High-grade NTC thermistors can achieve accuracy in the range of ±0.1–±0.5°C in targeted bands. For precise cell monitoring in EVs, procurement teams often require ≤±0.2°C. PTC thermistors are not typically selected for high-precision measurement; they are chosen for predictable resistance jumps at defined temperatures.
Smaller thermistor beads and thinner encapsulation yield faster response times—important for battery safety. For fast detection, choose low thermal mass NTC parts. For protection roles, the response of PTC devices must match expected surge and heating profiles.
NTC thermistors are non-linear. Systems either use lookup tables or apply curve linearization like the Steinhart–Hart equation. Ensure your BMS or ECU firmware supports this. PTC thermistors are simpler to use when acting as switches or current limiters.
| Parameter | NTC Thermistor | PTC Thermistor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary role | Precise temperature measurement | Protection / self-regulating heating |
| Typical accuracy | ±0.1–0.5°C | Switching threshold based |
| Typical response | Fast (ms to s) | Moderate (depends on design) |
| Common automotive use | Battery cell, coolant, HVAC | Pre-charge, motor protection, heaters |
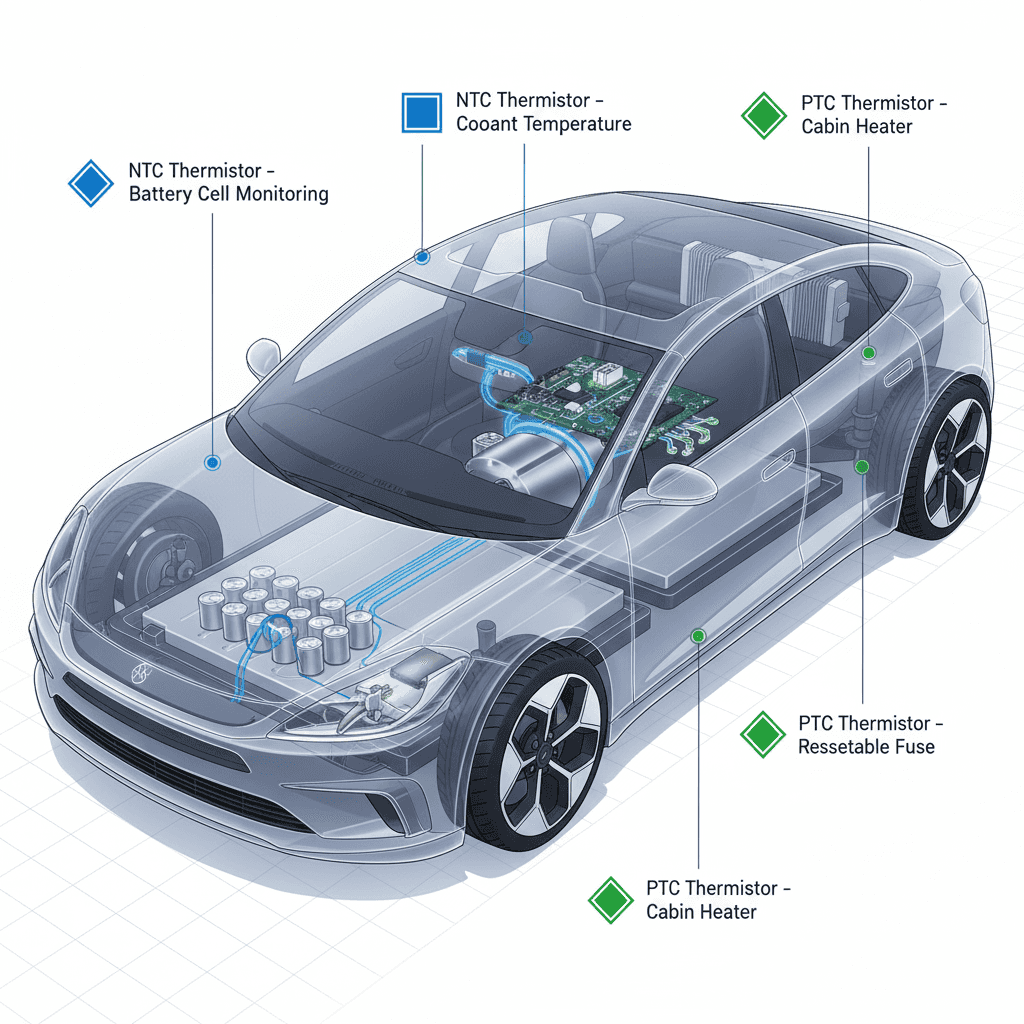
BMS designs demand high accuracy at cell level. An NTC thermistor automotive sensor mounted close to cells gives fast, precise readings for thermal balancing and charging control. For cell heating (to operate efficiently in cold climates), PTC heaters might be used—but the measurement remains NTC based.
Motor windings and inverter modules benefit from PTC sensors embedded in windings or housings. The PTC’s rising resistance can serve to trigger protective logic or disable the drive when temperatures exceed safe limits. In many motor designs, a PTC acts as a direct trip element for overtemperature.
Cabin air and evaporator sensors often use NTC thermistors for temperature feedback. Seat heaters and supplemental cabin heaters may incorporate PTC elements for safe, self-limiting heat output.
Use this checklist when evaluating suppliers and parts:
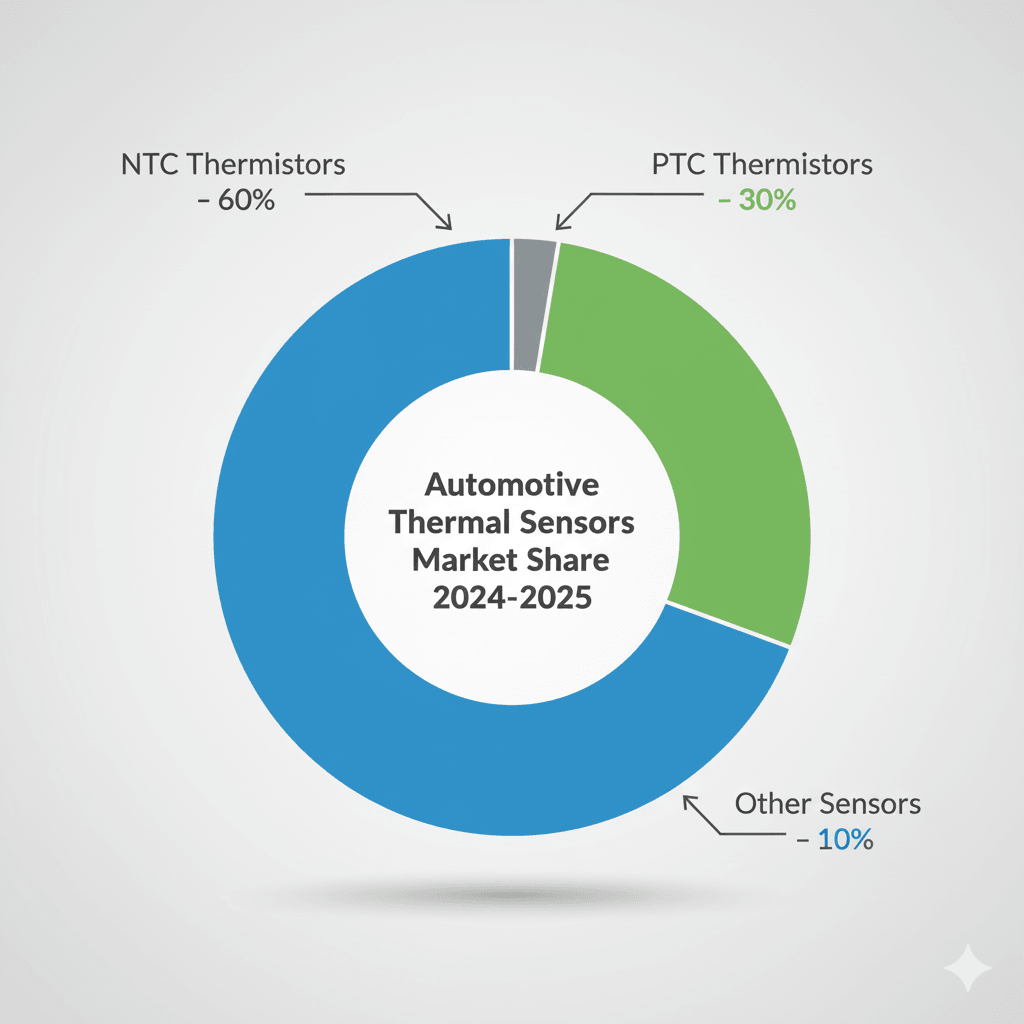
In 2025 procurement teams in the U.S. and Europe show consistent preferences:
A: No. NTC thermistor automotive parts and PTC thermistors serve complementary roles. Measurement needs demand NTC. Protection and self-limiting heating need PTC. Many vehicle systems use both.
A: Use the Steinhart–Hart equation or precomputed lookup tables. Modern BMS firmware supports this easily. If you prefer a simpler path, request calibration from the supplier at the part level.
A: For automotive applications request AEC-Q200 or equivalent test reports, ISO 9001 production evidence, RoHS/REACH material declarations, and test records for thermal cycling, vibration and salt spray when applicable.
Focusensing is a China-based factory specializing in resistance temperature sensors including NTC, PTC, RTD and digital sensors. The company focuses on B2B customers and offers customization, small-batch prototyping, and volume supply. Key advantages include:
See Focusensing product pages for details and datasheets: NTC thermistor catalog, PTC thermistor catalog, and custom temperature sensors.
A mid-size EV maker integrated high-precision NTC thermistors into cell modules. By specifying 10 kΩ @25°C NTC beads with ±0.2°C tolerance and glass bead encapsulation, the OEM improved thermal balancing during fast charge events and reduced temperature spread by 18%. Combined with faster BMS response logic, the pack achieved higher charge speed with no increase in thermal incidents.
For technical background on thermistor behavior and design, see Digi-Key’s primer: Digi-Key — Temperature Sensors & Thermistors. This resource provides practical formulas, circuit examples, and application notes that help engineers implement thermistors correctly.